Netdiscover is a simple ARP scanner which can be used to scan for live hosts in a network.
It is an active/passive address reconnaissance tool, mainly developed for those wireless networks without DHCP server, when you are wardriving. It can scan for multiple subnets also.
It simply produces the output in a live display (ncurse). This can be used in the first phases of a Pentest where you have access to a network. It can be also used on hub/switched networks.
Also Read – Address Resolution Protocol ARP Spoofing- Detection And Prevention
Built on top of libnet and libpcap, it can passively detect online hosts, or search for them, by actively sending ARP requests, it can also be used to inspect your network ARP traffic, or find network addresses using auto scan mode, which will scan for common local networks. Netdiscover is a simple and initial-recon tool which can be very handy.
Features:
- Simple ARP Scanner
- Works in both Active & Passive modes
- Produces a live display of identified hosts
- Able to scan multiple subnets
- Timing Options
Usage:
netdiscover [-i device] [-r range | -p] [-s time] [-n node] [-c count] [-f] [-S]
- -i device: your network device
- -r range: scan a given range instead of auto scan. 192.168.6.0/24,/16,/8
- -p passive mode do not send anything, only sniff
- -s time: time to sleep between each ARP request (miliseconds)
- -c count: number of times to send each ARP request (for nets with packet loss)
- -n node: last ip octet used for scanning (from 2 to 253)
- -S enable sleep time suppression between each request (hardcore mode)
- -f enable fast mode scan, saves a lot of time, recommended for auto
Simple Host discovery & Related Options:
Netdiscover runs simply by calling executing the command in auto mode
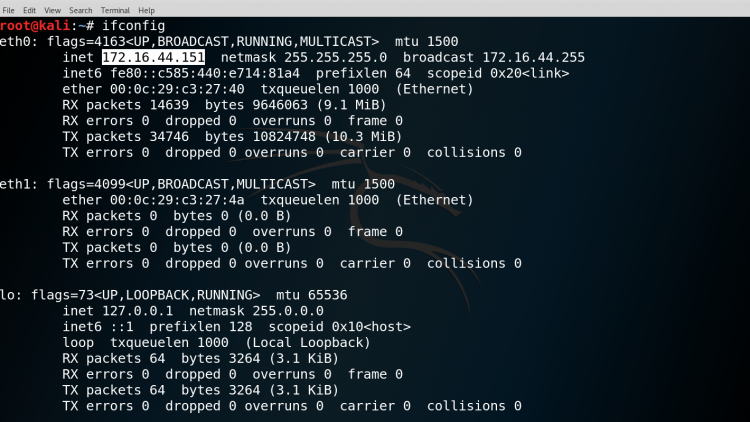
Firstly check the IP Address of the machine.
SYNTAX: ifconfig
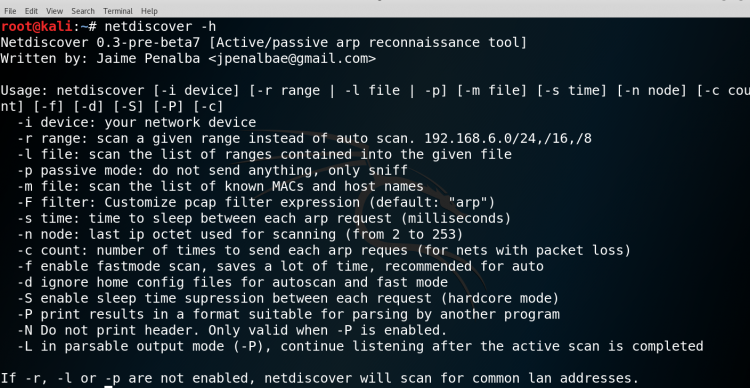
Then check the netdiscover help menu to understand the command more clearly.
SYNTAX: netdiscover -h
Then we will check the subnet of the IP address of machine to discover the host on the network.
Please do check the currently active interface that is the network device.
SYNTAX: netdiscover -i [interface name] -r [range of IP address]
$netdiscover -i eth0 -r 172.16.44.0/24

The output will show the active hosts that are in the network.
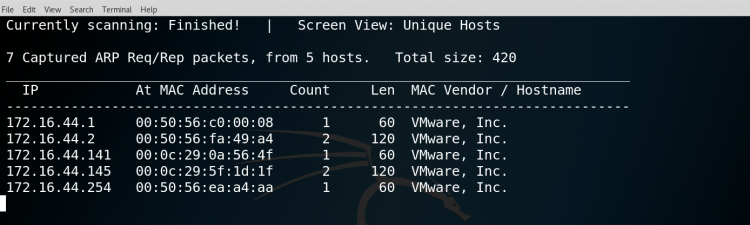
The output will contain the IP, MAC address, count i.e number of times to send each ARP request
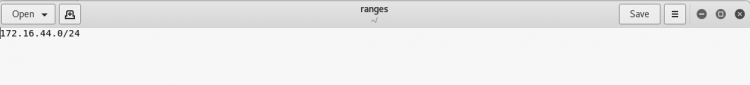
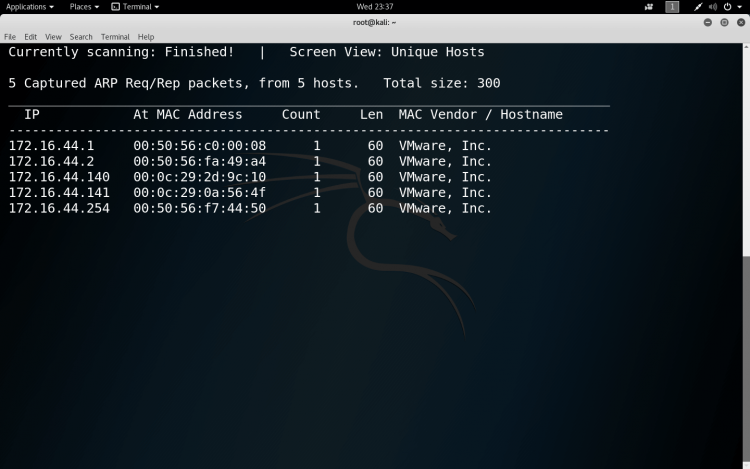
Multiple Ranges from a File
We can also scan for multiple ranges. This is useful when you have a large network with multiple subnets and networks. For this, simply we need specify all the ranges we want to scan in a file line-by-line.
SYNTAX:- netdiscover -l <file containing ranges>
*NOTE: make a file where the ranges are being saved
$netdiscover -l ranges
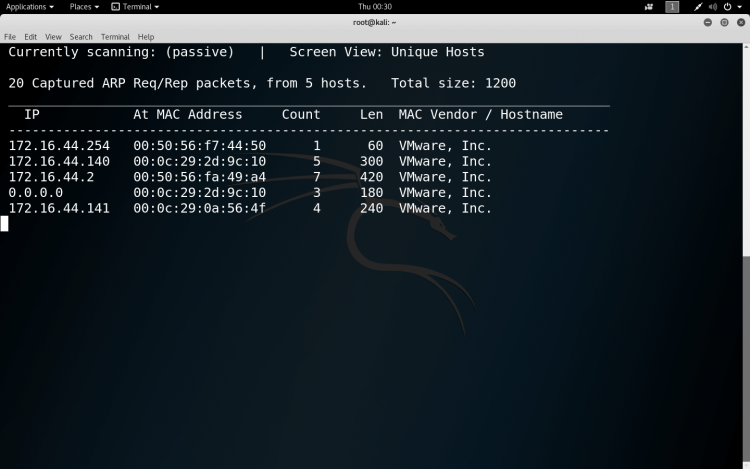
Passive Scanning
If we want to maintain a low profile to avoid getting caught, we can set up a passive ARP discovery; in this case we just sit sniffing the network traffic.
SYNTAX:- netdiscover -p
There are many scanners which we can be used to scan the network. The difference between those scanners and Netdiscover is that many other scanners send a lot of pings requests to all the IP in the subnet which gets flagged in the Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and your machine is blocked from accessing the network or your IP gets blacklisted in the IDS.
But on the other hand, Netdiscover uses simple ARP protocol to scan for hosts on the network it listens on the ARP requests that are being generated on the network and find which hosts are sending those requests.
NOTE: We should always use these tools in the constructive ways for learning not in a destructive way.