Preventing ransomware is not at all difficult, it really boils down to practicing safe security habits.
This means having a fundamental knowledge of cybersecurity awareness, which includes knowing not only the methods of staying safe, but the common attack methods that cyber criminals utilize.
In this article we will highlight a few of the most common methods cyber criminals use to infiltrate your network, and infect your machine with ransomware. In addition to the below, if you’re a business owner, you must also consider how well educated your team are on how to defend and protect your organisation against ransomware threats.
For more in-depth information on ransomware training for employees, we’d recommend this page from Inspired e-Learning. Ultimately you don’t want to be held hostage by hackers.
Infected Office Documents
This tactic is a combination of social engineering and phishing emails. Typically you’ll receive an email that appears to be some kind of important or official business, such as an outstanding invoice, or the IRS discovered money owed to you, or some variation of that old “Bank Error in Your Favor!” Monopoly card.
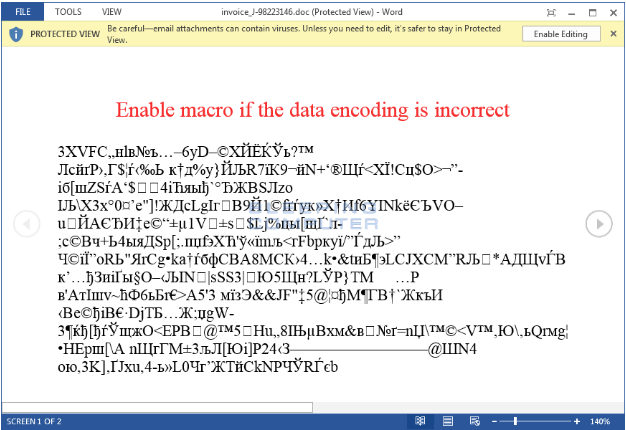
The email will have an attachment, typically a Microsoft Word document, or a PDF, most commonly. When you open the document, it will usually say something like “If you can’t read this document, please enable macros” or some variation of similar instructions. These instructions might be followed by strings of characters, to give the impression of “encrypted” information.
When you follow the instructions in the document, such as enabling macros, you’re actually turning the document into a script that proceeds to run. It will proceed to download the ransomware infection and encrypt all your files.
Also Read- Ransomware Attacks on Health Care
Preventing Ransomware this is as simple as not downloading and opening documents from strange emails, and certainly never following any instructions contained within. Furthermore, if you use Gmail, you don’t need to actually download the document to open it, as Gmail offers a “preview” mode that will let you see the contents of a document without downloading and opening it.
Remote Desktop Protocol Access
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is software typically used by IT specialists to remotely access machines, for the purpose of troubleshooting or configuring machines without actually sitting in front of them. RDP software is highly useful for that purpose.
Unfortunately, RDP software can easily be used for malicious activity. What typically happens is that, because RDP software relies on specific ports being open on the network to make a connection, cybercriminals will scan various ports to find a list of machines with those ports open and available to RDP software.
Once they’ve gathered a list of machines, they’ll use a password database to try and brute force their way into those machines, effectively giving them complete remote control of the computer.
Preventing this requires some knowledge of how firewalls operate, and configuring ports. Because cybercriminals tend to focus on the most common and generic ports used for RDP software, it’s a wise idea to use alternate ports. You should also use strong passwords that cannot be easily brute forced. MalwareBytes has a good blog article with more information on preventing RDP attacks.
Malicious website plugins and advertisements
Downloads can be a common source of infection, especially if you download things such as pirated software. However, you can be infected simply by visiting websites that contain malicious scripts and plugins.
Believe it or not, banner advertisements, even on reputable websites, can be a source of infection. Because website owners don’t typically control what advertisements are shown on their website, but belong to an advertising network, cybercriminals figured out a way to buy up ad space on even popular, reputable websites.
They then trick the ad network into displaying advertisements that contain malicious code, which can be executed by visitors simply visiting the website, no downloading necessary.
This malvertising (portmanteau of ‘malware’ and ‘advertising’) typically relies on vulnerabilities in the user’s browser, outdated JavaScript or Flash, or other security loopholes.
Thus, preventing this form of attack can depend on having a good ad blocker, disabling JavaScript / Flash on all websites except those you explicitly trust, and having a good antivirus software that can scan websites for threats.