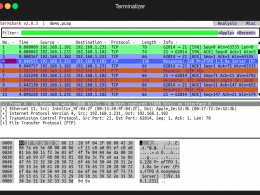
Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer.
It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education.
Also read – How To Analyse And Capture The Packets in Wireshark
Following Wireshark Commands are using for Network analysis.
Capture interface:
-i <interface> name or idx of interface (def: first non-loopback)
-f <capture filter> packet filter in libpcap filter syntax
-s <snaplen> packet snapshot length (def: 65535)
-p don’t capture in promiscuous mode
-k start capturing immediately (def: do nothing)
-Q quit Wireshark after capturing
-S update packet display when new packets are captured
-l turn on automatic scrolling while -S is in use
-B <buffer size> size of kernel buffer (def: 1MB)
-y <link type> link layer type (def: first appropriate)
-D print list of interfaces and exit
-L print list of link-layer types of iface and exit
–list-time-stamp-types print list of timestamp types for iface and exit
Capture stop conditions:
-c <packet count> stop after n packets (def: infinite)
-a <autostop cond.> … duration:NUM – stop after NUM seconds
filesize:NUM – stop this file after NUM KB
files:NUM – stop after NUM files
Capture output:
-b <ringbuffer opt.> … duration:NUM – switch to next file after NUM secs
filesize:NUM – switch to next file after NUM KB
files:NUM – ringbuffer: replace after NUM files
RPCAP options:
-A <user>:<password> use RPCAP password authentication
Input file:
-r <infile> set the filename to read from (no pipes or stdin!)
Processing:
-R <read filter> packet filter in Wireshark display filter syntax
-n disable all name resolutions (def: all enabled)
-N <name resolve flags> enable specific name resolution(s): “mntdv”
-d <layer_type>==<selector>,<decode_as_protocol> …
“Decode As”, see the man page for details
Example: tcp.port==8888,http
–disable-protocol <proto_name>
disable dissection of proto_name
–enable-heuristic <short_name>
enable dissection of heuristic protocol
–disable-heuristic <short_name>
disable dissection of heuristic protocol
User interface Wireshark Commands:
-C <config profile> start with specified configuration profile
-Y <display filter> start with the given display filter
-g <packet number> go to specified packet number after “-r”
-J <jump filter> jump to the first packet matching the (display)
filter
-j search backwards for a matching packet after “-J”
-m <font> set the font name used for most text
-t a|ad|d|dd|e|r|u|ud output format of time stamps (def: r: rel. to first)
-u s|hms output format of seconds (def: s: seconds)
-X <key>:<value> eXtension options, see man page for details
-z <statistics> show various statistics, see man page for details
Output:
-w <outfile|-> set the output filename (or ‘-‘ for stdout)
Miscellaneous Wireshark Commands:
-h display this help and exit
-v display version info and exit
-P <key:path> persconf:path – personal configuration files
persdata:path – personal data files
-o <name>:<value> … override preference or recent setting
-K <keytab> keytab file to use for kerberos decryption
Logical operators are available for all filtering.
Example: http & ip.src == 192.168.0.1
Management Frame: The frame for the connection between the network device and the client.
Control Frame: Controls the integrity of data traffic between the network device and the client.
Data Frame: The frame on which the original data is transferred.
Only to show the outgoing packets from the management frame.
wlan.fc.type==0
To show incoming, outgoing packets through control frame.
wlan.fc.type==1
To show packets transferred over the data frame.
wlan.fc.type==2
Association lists the requests.
wlan.fc.type_subtype==0
Association lists the answers.
wlan.fc.type_subtype==1
Probe lists requests.
wlan.fc.type_subtype==4
Lists the probe responses.
wlan.fc.type_subtype==5
Lists Beacon signals / waves.
wlan.fc.type_subtype==8
Lists the Authentication requests.
wlan.fc.type_subtype==11
Lists deauthentication requests.
wlan.fc.type_subtype==12
TCP lists the outgoing packets to the xx port.
tcp.port == xx
TCP lists packages with the Source xx port.
tcp.srcport == xx
TCP lists packages with a destination xx port.
tcp.dstport == xx
UDP lists the outgoing packets to the xx port.
udp.port == xx
UDP lists packets with a destination xx port.
udp.srcport == xx
UDP lists packages that have the Source xx port.
udp.dstport == xx
Lists the HTTP Get requests.
http.request
Lists packages for the source or destination mac address.
wlan.addr == MAC-Address
The source lists packages that have a mac address.
wlan.sa == MAC-Address
Lists packages that have a target mac address.
wlan.da == MAC-Address
You can download Wireshark from here