Cyber Attack On INDIAN official websites are rising, most attacks from the US, China and Russia reportedly.
According to Financial Express, a report sent to the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) and other security official agencies by a department under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and said that the maximum number of Cyber attacks on Indian official websites are from China, US and Russia.
The report warns that there is a possibility for Malicious actors from Pakistan using German and Canadian cyberspace from intruding into India Cyberspace and carrying out malicious activities.
In August 2018, we have reported, The Hackers Stole Rupees 94 Crore From Indian Cosmos Bank, where Money was transferred outside the country and Bank servers were hacked through Malware Attack.
Last year, the biggest attack was WannaCry Ransomware. WannaCry was affecting computers worldwide. It became the biggest Cyber Threat worldwide. Approx 200,000 computers and 150 countries hit till now. Which including companies and National Health service
According to the report, the Cyber attacks on an INDIAN website are as follows in percentage.
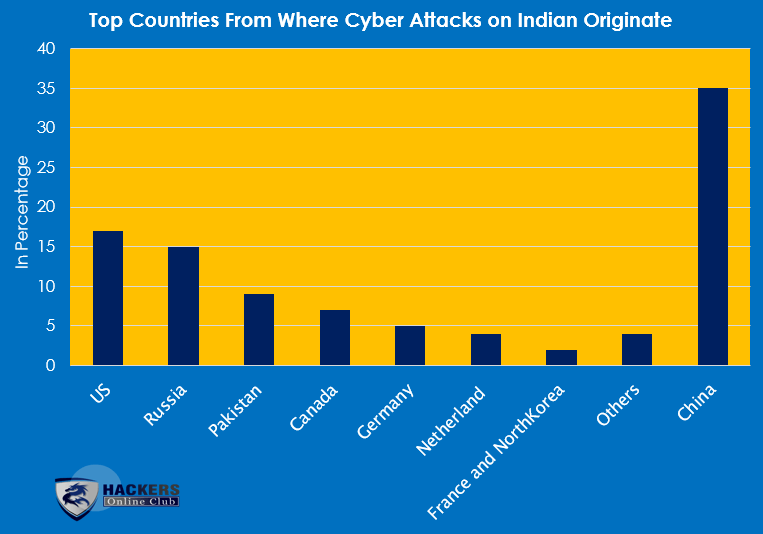
- US 17 percent
- Russia 15 percent
- Pakistan 9 percent
- Canada 7 percent
- Germany 5 percent
- Netherlands 4 percent
- France and North Korea 2 percent
- Others 4 percent
Top Affected Companies
- Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC)
- National Informatics Centre (NIC)
- Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC)
- Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS)
Many of the biggest government officials impacted by the malicious activities have been identified, and they have been advised to take appropriate preventive action.
Top Affected Indian Banks
- Punjab National Bank (PNB)
- Oriental Bank of Commerce (OBC)
- State Bank of India (SBI)
- State data centres (particularly in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka)
According to IE report,
The activities relating to intruding into the cyberspace are being regularly monitored. China continues to be intruding the cyberspace in a significant way followed by the US and Russia. It has also been observed that intruding activities are coming from Canadian and German cyberspace most possibly suspected to have originated from Pakistan actors to target Indian websites.
They are targeting to victims by sending spear phishing emails with malware attachments. Phishing attacks are usually in the form of an email from a trusted source where they ask for personal details such as bank details personal details, passwords,” explained an official.
According to CERT, China has made the highest number of attacks on the Indian official websites. By analyzing the data for April and June, CERT was found 35 percent of intruding activity from Chinese hackers.
How can we Protect?
- Do not click on an unknown link and the attachment in E-mail.
- Avoid to use the same password.
- Use special Keywords in Password.
- Change your ATM PIN regularly.
- Don’t give any personal information on the phone.
- The Bank never asks your personal info on call.
What are the Cyber Laws In INDIA:
- Information Technology (IT) Act 2000
- Indian Penal Code (IPC) 1860
SECTIONS UNDER IT ACT 2000:
Sec. 65- Tampering with Computer source documents
Whoever intentionally or knowingly destroys, conceals or changes any computer’s source code that is used for a computer, computer program, and computer system or computer network.
Sec. 66- Hacking with computer systems, data alteration
Whoever with the purpose or intention to cause any loss, damage or to destroy, delete or to alter any information that resides in any person’s computer.
Sec.67- Publishing obscene information:
Whoever transmits or publishes or cause to publish any obscene material in electronic form. Any material that is vulgar or appeals to be lubricious or is meant to corrupt any individual who is likely to have regard to all relevant circumstances to read or to see or to hear the matter that contained in it shall be sentenced on the first convict with a term that may extend up to five years of imprisonment.
Sec. 68- Failure/refusal to comply with orders:
The Controller may, by order, direct a Certifying Authority or any employee of such Authority to take such measures or cease carrying on such activities as specified in the order if those are necessary to ensure compliance with the provisions of this Act, rules or any regulations made thereunder. Any person who fails to comply with any such order shall be guilty of an offence.
Penalty- Imprisonment up to three years, or/and with fine up to ₹200,000
Sec. 69- Failure/Refusal to decrypt data
If the Controller is satisfied that it is necessary or expedient so to do in the interest of the sovereignty or integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign Stales or public order or for preventing incitement to the commission of any cognizable offence, for reasons to be recorded in writing, by order, direct any agency of the Government to intercept any information transmitted through any computer resource. The subscriber or any person in charge of the computer resource shall, when called upon by any agency which has been directed, must extend all facilities and technical assistance to decrypt the information. The subscriber or any person who fails to assist the agency referred is deemed to have committed a crime.
Penalty- Imprisonment up to seven years and a possible fine.
Sec. 70- Securing access or attempting to secure access to a protected system
The appropriate Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, declare that any computer, computer system or computer network to be a protected system.
The appropriate Government may, by order in writing, authorise the persons who are authorised to access protected systems. If a person who secures access or attempts to secure access to a protected system, then he is committing an offence.
Penalty- Imprisonment up to ten years, or/and with a fine.
Sec. 71- Misrepresentation
If anyone makes any misrepresentation to, or suppresses any material fact from, the Controller or the Certifying Authority for obtaining any license or Digital Signature Certificate.
Penalty- Imprisonment up to three years, or/and with fine up to 100,000 INR
Sec.72- Breach of Confidentiality and Privacy
Any person, who has secured access to any electronic record, book, register, correspondence, information, document or other material without the consent of the person concerned, discloses such electronic record, book, register, correspondence, information, document or other material to any other person shall be punished with imprisonment for a term which may extend to two years, or with a fine which may extend to one lakh rupees, or with both.
Sec. 73- Publishing false digital signature certificates
No person shall publish a false Electronic Signature Certificate or otherwise make it available to any other person despite knowing the following points: (a). The Certifying Authority listed in the certificate has not issued it; or (b) The subscriber listed in the certificate has not accepted it; or (c) The certificate has been revoked or suspended unless such publication is for the purpose of verifying a digital signature created prior to such suspension or revocation.