Cyber attackers are exploiting a WebLogic vulnerability to install a new Sodinokibi Ransomware. Cisco Talos Intelligence group explains in their blog.
What is Sodinokibi Ransomware?
Sodinokibi attempts to encrypt data in a user’s directory and delete shadow copy backups to make data recovery more difficult.
Sodinokibi Ransomware could be spread through email attachment or form malicious link and exploit WebLogic server vulnerability.
Once the attackers found a vulnerable server, they sent an HTTP POST request that request contained a PowerShell command to execute the ransomware file.
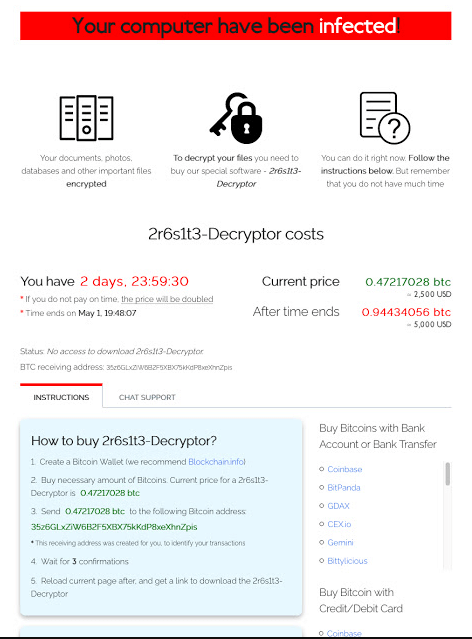
After the downloaded, the ransomware encrypt the systems and asked a ransom to victim. It is redirect to a page on the TOR network domain, which was registered on 31st March 2019.
Last week Oracle patched the Weblogic zero day vulnerability and assigned CVE-2019-2725. This Security Alert was released in response to a recently-disclosed vulnerability affecting Oracle WebLogic Server. This vulnerability affects a number of versions of Oracle WebLogic Server and has received a CVSS Base Score of 9.8. WebLogic Server customers should refer to the Security Alert Advisory for information on affected versions and how to obtain the required patches.
Cisco’s Incident Response (IR) team, along with Cisco Talos, are actively investigating these attacks and Sodinokibi Ransomware.
Initial stages of the ransomware attack occurred on April 25, the day before Oracle released their update. This was a trial to see whether the server was exploitable.
On April 26, 2019, the attackers made an HTTP connection to a different vulnerable server, requesting the AsyncResponderService of the Oracle WebLogic Server.
“After finishing deploying Sodinokibi ransomware inside the victim’s network, the attackers followed up with an additional CVE-2019-2725 exploit attempt approximately eight hours later. However, this time, the attackers chose to distribute Gandcrab v5.2.
Researchers find it strange the attackers would choose to distribute additional, different ransomware on the same target. Sodinokibi being a new flavor of ransomware, perhaps the attackers felt their earlier attempts had been unsuccessful and were still looking to cash in by distributing Gandcrab.”
According to Threatpost, the Researchers also noted that, once downloaded, the malicious file executed vssadmin.exe, a legitimate utility bundled with Windows that enables allows administrators to manage the shadow copies that are on the computer. Shadow copies are a technology that enables systems to take automatic backup copies of computer files.
Because attackers executed this feature, it allows them to access and delete the automatic backups – making it harder for victims to recover their data: “This action is a common [tactic] of ransomware to prevent users from easily recovering their data,” researchers said. “It attempts to delete default Windows backup mechanisms, otherwise known as ‘shadow copies,’ to prevent recovery of the original files from these backups.”











