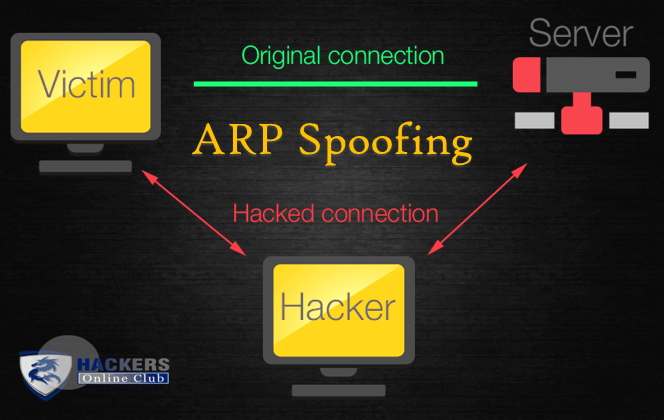
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) spoofing is a type of cyber attack wherein attackers send malicious ARP Packets to a default gateway over the Local Area network (LAN), exploiting it in a way to link their own MAC address with the IP address of the gateway device.
Generally, the aim to associate the attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of another host, such as the default gateway, is to cause any traffic meant for that IP address to be sent through the attacker instead.
ARP spoofing may allow an attacker to intercept data frames on a network, modify the traffic, or stop all the traffic. Often the attack is used as an opening for other network based attacks, such as denial of service, man in the middle, or session hijacking attacks.
The attack can only be used on networks that use ARP, and requires attacker to have direct access to the local network segment to be attacked. ARP is a widely used stateless communications protocol for resolving Internet layer addresses into link layer addresses.
Network hosts will automatically cache any ARP replies they receive, regardless of whether network hosts requested them. Even ARP entries that have not yet expired will be overwritten when a new ARP reply packet is received.
There is no method in the ARP protocol by which a host can authenticate the peer from which the packet originated. This behavior is the vulnerability that allows ARP spoofing to occur.
ARP spoofing attack
The basic principle behind ARP spoofing is to exploit the lack of authentication in the ARP protocol by sending spoofed ARP messages onto the LAN.
ARP spoofing attacks can be run from a compromised host on the LAN, or from an attacker’s machine that is connected directly to the target LAN.
Generally, the goal of the attack is to associate the attacker’s host MAC address with the IP address of a target host, so that any traffic meant for the target host will be sent to the attacker’s host.
The attacker may choose to inspect the packets (spying), while forwarding the traffic to the actual default destination to avoid discovery, modify the data before forwarding it (man-in-the-middle attack), or launch a denial-of-service attack by causing some or all of the packets on the network to be dropped.
ARP Spoofing Detection And Prevention
Software that detects ARP spoofing generally relies on some form of certification or cross-checking of ARP responses.
Uncertified ARP responses are then blocked. These techniques may be integrated with the DHCP server so that both dynamic and static IP addresses are certified.
Check the following detection software application
- shARP: An Anti ARP-Spoofing Application Software
- SCUTUM – Linux Automatic ARP (TCP / UDP / ICMP) Firewall
The existence of multiple IP addresses associated with a single MAC address may indicate an ARP spoof attack, although there are legitimate uses of such a configuration. In a more passive approach a device listens for ARP replies on a network, and sends a notification via email when an ARP entry changes.
How To Protect ARP Spoofing attack?
- Use VPN
Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypt the network tunnel that blocks your activity and protect you from spoofing attack. We are recommending do not use Public Wi-Fi or hotspots, it might be chanced for Man In The Middle attack. VPN can protect you for safer way to use internet private network.
- Static ARP
If you have two hosts, then setting up a static ARP entry creates a permanent entry in your ARP cache that can help add a layer of protection from spoofing.
- Avoid Trust Relationship
Trust relationship rely on IP Addresses for authentication, you must need to avoid. In company you should create private logins, and password to identify the users through protection policies could be layer of protection.
- Packet Filtering
Packet filtering is a type of firewall used to control network access by monitoring incoming and outgoing packets.
A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external network, such as the Internet. Packets may be filtered by source and destination network addresses, protocol, source and destination port numbers.
Also See – ARP-Scan Command To Scan The Local Network